Indus Waters Treaty: History, Key Provisions, and Ongoing Disputes Between India and Pakistan
Indus Waters Treaty is one of the most significant water-sharing agreements in the world and a cornerstone of relations between India and Pakistan. Signed in 1960, the treaty has successfully managed the distribution of the Indus River system for more than six decades, even during times of political tension. Today, however, it faces new challenges as both nations grapple with climate change, population growth, and competing water demands. Newsmax

History of the Indus Waters Treaty
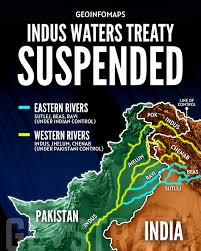
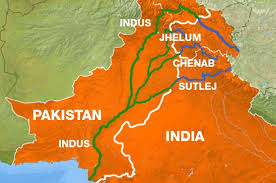
After the partition of British India in 1947, the Indus River system — vital for agriculture and livelihoods — was divided between the two newly formed countries, India and Pakistan. Disputes soon arose over water usage and control. To resolve the issue, years of negotiation led to the signing of the Indus Waters Treaty in 1960, brokered with international support.
Under the treaty, the six rivers of the Indus basin were divided between the two nations. The three eastern rivers — Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej — were allocated to India, while the three western rivers — Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab — were granted to Pakistan. The agreement also established mechanisms for cooperation, data sharing, and dispute resolution. Newsmax
Key Provisions of the Treaty
-
Water Allocation:
-
India controls the waters of the eastern rivers.
-
Pakistan controls the waters of the western rivers, with limited use allowed for India in agriculture, transport, and hydroelectric projects.
-
-
Permanent Indus Commission:
A joint commission was formed to oversee the implementation of the treaty, share data, and discuss technical matters. -
Dispute Resolution Mechanism:
Any disagreement is first discussed by the commission. If unresolved, it can be referred to neutral experts or international arbitration. -
Infrastructure Rights:
India has the right to construct run-of-the-river hydroelectric projects on the western rivers, provided they do not affect the water flow to Pakistan. Newsmax
Significance of the Indus Waters Treaty
The Indus Waters Treaty is often cited as a model of successful transboundary water management. Despite wars and political disputes between India and Pakistan, the treaty has remained in force. It ensures the continued flow of water to millions of people who depend on the Indus basin for agriculture, drinking water, and industry.
The agreement also symbolizes the possibility of cooperation even in strained diplomatic environments. For decades, it has acted as a stabilizing factor in South Asia’s geopolitics.
Current Challenges and Disputes
In recent years, the Indus Waters Treaty has faced renewed strain. Pakistan has raised concerns over several Indian hydroelectric projects, claiming they violate treaty terms by altering water flow. India, on the other hand, insists that its projects comply with the treaty’s technical specifications.
Climate change and rapid population growth have further complicated water management. The shrinking of glaciers feeding the Indus basin and increased water demand are adding pressure on both sides to reassess their water security strategies. Newsmax

The Way Forward
Experts emphasize the need for continuous dialogue, transparency, and modernization of the treaty to meet 21st-century challenges. Enhancing data sharing, adopting sustainable water technologies, and promoting joint research could strengthen cooperation.
Both India and Pakistan have much to gain from preserving the spirit of the Indus Waters Treaty. Water is not just a resource — it is a shared lifeline for millions across the region. Newsmax
Conclusion
The Indus Waters Treaty stands as a rare example of enduring cooperation between two neighboring nations with a complex history. As environmental and political pressures increase, maintaining and updating this vital agreement is essential for peace, stability, and sustainable water management in South Asia. Visit Now